Table Of Contents
VKeyboard¶
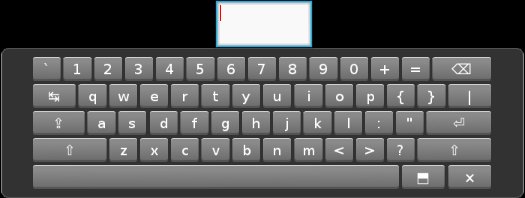
New in version 1.0.8.
VKeyboard is an onscreen keyboard for Kivy. Its operation is intended to be transparent to the user. Using the widget directly is NOT recommended. Read the section Request keyboard first.
Modes¶
This virtual keyboard has a docked and free mode:
docked mode (
VKeyboard.docked= True) Generally used when only one person is using the computer, like a tablet or personal computer etc.free mode: (
VKeyboard.docked= False) Mostly for multitouch surfaces. This mode allows multiple virtual keyboards to be used on the screen.
If the docked mode changes, you need to manually call
VKeyboard.setup_mode() otherwise the change will have no impact.
During that call, the VKeyboard, implemented on top of a
Scatter, will change the
behavior of the scatter and position the keyboard near the target (if target
and docked mode is set).
Layouts¶
The virtual keyboard is able to load a custom layout. If you create a new
layout and put the JSON in <kivy_data_dir>/keyboards/<layoutid>.json,
you can load it by setting VKeyboard.layout to your layoutid.
The JSON must be structured like this:
{
"title": "Title of your layout",
"description": "Description of your layout",
"cols": 15,
"rows": 5,
...
}
Then, you need to describe the keys in each row, for either a “normal”, “shift” or a “special” (added in version 1.9.0) mode. Keys for this row data must be named normal_<row>, shift_<row> and special_<row>. Replace row with the row number. Inside each row, you will describe the key. A key is a 4 element list in the format:
[ <text displayed on the keyboard>, <text to put when the key is pressed>,
<text that represents the keycode>, <size of cols> ]
Here are example keys:
# f key
["f", "f", "f", 1]
# capslock
["↹", " ", "tab", 1.5]
Finally, complete the JSON:
{
...
"normal_1": [
["`", "`", "`", 1], ["1", "1", "1", 1], ["2", "2", "2", 1],
["3", "3", "3", 1], ["4", "4", "4", 1], ["5", "5", "5", 1],
["6", "6", "6", 1], ["7", "7", "7", 1], ["8", "8", "8", 1],
["9", "9", "9", 1], ["0", "0", "0", 1], ["+", "+", "+", 1],
["=", "=", "=", 1], ["⌫", null, "backspace", 2]
],
"shift_1": [ ... ],
"normal_2": [ ... ],
"special_2": [ ... ],
...
}
Request Keyboard¶
The instantiation of the virtual keyboard is controlled by the configuration. Check keyboard_mode and keyboard_layout in the Configuration object.
If you intend to create a widget that requires a keyboard, do not use the
virtual keyboard directly, but prefer to use the best method available on
the platform. Check the request_keyboard()
method in the Window.
If you want a specific layout when you request the keyboard, you should write something like this (from 1.8.0, numeric.json can be in the same directory as your main.py):
keyboard = Window.request_keyboard(
self._keyboard_close, self)
if keyboard.widget:
vkeyboard = self._keyboard.widget
vkeyboard.layout = 'numeric.json'
- class kivy.uix.vkeyboard.VKeyboard(**kwargs)¶
Bases:
kivy.uix.scatter.ScatterVKeyboard is an onscreen keyboard with multitouch support. Its layout is entirely customizable and you can switch between available layouts using a button in the bottom right of the widget.
- Events:
- on_key_down: keycode, internal, modifiers
Fired when the keyboard received a key down event (key press).
- on_key_up: keycode, internal, modifiers
Fired when the keyboard received a key up event (key release).
- collide_margin(x, y)¶
Do a collision test, and return True if the (x, y) is inside the vkeyboard margin.
- on_touch_down(touch)¶
Receive a touch down event.
- Parameters:
- touch:
MotionEventclass Touch received. The touch is in parent coordinates. See
relativelayoutfor a discussion on coordinate systems.
- touch:
- Returns:
bool If True, the dispatching of the touch event will stop. If False, the event will continue to be dispatched to the rest of the widget tree.
- on_touch_up(touch)¶
Receive a touch up event. The touch is in parent coordinates.
See
on_touch_down()for more information.
- refresh(force=False)¶
(internal) Recreate the entire widget and graphics according to the selected layout.
- setup_mode(*largs)¶
Call this method when you want to readjust the keyboard according to options:
dockedor not, with attachedtargetor not:If
dockedis True, it will callsetup_mode_dock()If
dockedis False, it will callsetup_mode_free()
Feel free to overload these methods to create new positioning behavior.
- setup_mode_dock(*largs)¶
Setup the keyboard in docked mode.
Dock mode will reset the rotation, disable translation, rotation and scale. Scale and position will be automatically adjusted to attach the keyboard to the bottom of the screen.
Note
Don’t call this method directly, use
setup_mode()instead.
- setup_mode_free()¶
Setup the keyboard in free mode.
Free mode is designed to let the user control the position and orientation of the keyboard. The only real usage is for a multiuser environment, but you might found other ways to use it. If a
targetis set, it will place the vkeyboard under the target.Note
Don’t call this method directly, use
setup_mode()instead.
