Table Of Contents
- Animation
- Simple animation
- Multiple properties and transitions
- Sequential animation
- Parallel animation
- Repeating animation
AnimationAnimationTransitionAnimationTransition.in_back()AnimationTransition.in_bounce()AnimationTransition.in_circ()AnimationTransition.in_cubic()AnimationTransition.in_elastic()AnimationTransition.in_expo()AnimationTransition.in_out_back()AnimationTransition.in_out_bounce()AnimationTransition.in_out_circ()AnimationTransition.in_out_cubic()AnimationTransition.in_out_elastic()AnimationTransition.in_out_expo()AnimationTransition.in_out_quad()AnimationTransition.in_out_quart()AnimationTransition.in_out_quint()AnimationTransition.in_out_sine()AnimationTransition.in_quad()AnimationTransition.in_quart()AnimationTransition.in_quint()AnimationTransition.in_sine()AnimationTransition.linear()AnimationTransition.out_back()AnimationTransition.out_bounce()AnimationTransition.out_circ()AnimationTransition.out_cubic()AnimationTransition.out_elastic()AnimationTransition.out_expo()AnimationTransition.out_quad()AnimationTransition.out_quart()AnimationTransition.out_quint()AnimationTransition.out_sine()
Animation¶
Animation and AnimationTransition are used to animate
Widget properties. You must specify at least a
property name and target value. To use an Animation, follow these steps:
Setup an Animation object
Use the Animation object on a Widget
Simple animation¶
To animate a Widget’s x or y position, simply specify the target x/y values where you want the widget positioned at the end of the animation:
anim = Animation(x=100, y=100)
anim.start(widget)
The animation will last for 1 second unless duration is specified.
When anim.start() is called, the Widget will move smoothly from the current
x/y position to (100, 100).
Multiple properties and transitions¶
You can animate multiple properties and use built-in or custom transition
functions using transition (or the t= shortcut). For example,
to animate the position and size using the ‘in_quad’ transition:
anim = Animation(x=50, size=(80, 80), t='in_quad')
anim.start(widget)
Note that the t= parameter can be the string name of a method in the
AnimationTransition class or your own animation function.
Sequential animation¶
To join animations sequentially, use the ‘+’ operator. The following example will animate to x=50 over 1 second, then animate the size to (80, 80) over the next two seconds:
anim = Animation(x=50) + Animation(size=(80, 80), duration=2.)
anim.start(widget)
Parallel animation¶
To join animations in parallel, use the ‘&’ operator. The following example will animate the position to (80, 10) over 1 second, whilst in parallel animating the size to (800, 800):
anim = Animation(pos=(80, 10))
anim &= Animation(size=(800, 800), duration=2.)
anim.start(widget)
Keep in mind that creating overlapping animations on the same property may have
unexpected results. If you want to apply multiple animations to the same
property, you should either schedule them sequentially (via the ‘+’ operator or
using the on_complete callback) or cancel previous animations using the
cancel_all method.
Repeating animation¶
New in version 1.8.0.
Note
This is currently only implemented for ‘Sequence’ animations.
To set an animation to repeat, simply set the Sequence.repeat
property to True:
anim = Animation(...) + Animation(...)
anim.repeat = True
anim.start(widget)
For flow control of animations such as stopping and cancelling, use the methods already in place in the animation module.
- class kivy.animation.Animation(**kw)[source]¶
Bases:
kivy.event.EventDispatcherCreate an animation definition that can be used to animate a Widget.
- Parameters:
- duration or d: float, defaults to 1.
Duration of the animation, in seconds.
- transition or t: str or func
Transition function for animate properties. It can be the name of a method from
AnimationTransition.- step or s: float
Step in milliseconds of the animation. Defaults to 0, which means the animation is updated for every frame.
To update the animation less often, set the step value to a float. For example, if you want to animate at 30 FPS, use s=1/30.
- Events:
- on_start: animation, widget
Fired when the animation is started on a widget.
- on_complete: animation, widget
Fired when the animation is completed or stopped on a widget.
- on_progress: animation, widget, progression
Fired when the progression of the animation is changing.
Changed in version 1.4.0: Added s/step parameter.
Changed in version 1.10.0: The default value of the step parameter was changed from 1/60. to 0.
- property animated_properties¶
Return the properties used to animate.
- cancel(widget)[source]¶
Cancel the animation previously applied to a widget. Same effect as
stop, except the on_complete event will not be triggered!New in version 1.4.0.
- static cancel_all(widget, *largs)[source]¶
Cancel all animations that concern a specific widget / list of properties. See
cancel.Example:
anim = Animation(x=50) anim.start(widget) # and later Animation.cancel_all(widget, 'x')
New in version 1.4.0.
Changed in version 2.1.0: If the parameter
widgetis None, all animated widgets will be the target and cancelled. Iflargsis also given, animation of these properties will be canceled for all animated widgets.
- cancel_property(widget, prop)[source]¶
Even if an animation is running, remove a property. It will not be animated further. If it was the only/last property being animated, the animation will be canceled (see
cancel)New in version 1.4.0.
- property duration¶
Return the duration of the animation.
- have_properties_to_animate(widget)[source]¶
Return True if a widget still has properties to animate.
New in version 1.8.0.
- stop(widget)[source]¶
Stop the animation previously applied to a widget, triggering the on_complete event.
- static stop_all(widget, *largs)[source]¶
Stop all animations that concern a specific widget / list of properties.
Example:
anim = Animation(x=50) anim.start(widget) # and later Animation.stop_all(widget, 'x')
- stop_property(widget, prop)[source]¶
Even if an animation is running, remove a property. It will not be animated further. If it was the only/last property being animated, the animation will be stopped (see
stop).
- property transition¶
Return the transition of the animation.
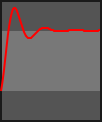
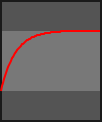
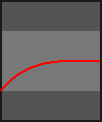
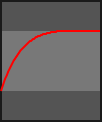
- class kivy.animation.AnimationTransition[source]¶
Bases:
builtins.objectCollection of animation functions to be used with the Animation object. Easing Functions ported to Kivy from the Clutter Project https://developer.gnome.org/clutter/stable/ClutterAlpha.html
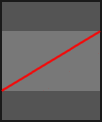
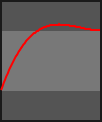
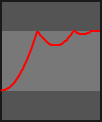
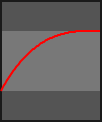
The progress parameter in each animation function is in the range 0-1.