Table Of Contents
Multitexture Example¶
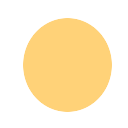
This example blends two textures: the image mtexture1.png of the letter K and the image mtexture2.png of an orange circle. You should see an orange K clipped to a circle. It uses a custom shader, written in glsl (OpenGL Shading Language), stored in a local string.
Note the image mtexture1.png is a white ‘K’ on a transparent background, which makes it hard to see.
File canvas/multitexture.py¶
'''
Multitexture Example
====================
This example blends two textures: the image mtexture1.png of the letter K
and the image mtexture2.png of an orange circle. You should see an orange
K clipped to a circle. It uses a custom shader, written in glsl
(OpenGL Shading Language), stored in a local string.
Note the image mtexture1.png is a white 'K' on a transparent background, which
makes it hard to see.
'''
from kivy.clock import Clock
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.widget import Widget
from kivy.uix.floatlayout import FloatLayout
from kivy.lang import Builder
from kivy.core.window import Window
from kivy.graphics import RenderContext, Color, Rectangle, BindTexture
fs_multitexture = '''
$HEADER$
// New uniform that will receive texture at index 1
uniform sampler2D texture1;
void main(void) {
// multiple current color with both texture (0 and 1).
// currently, both will use exactly the same texture coordinates.
gl_FragColor = frag_color * \
texture2D(texture0, tex_coord0) * \
texture2D(texture1, tex_coord0);
}
'''
kv = """
<MultitextureLayout>:
Image:
source: "mtexture1.png"
size_hint: .3,.3
id: 1
pos: 0,200
Image:
source: "mtexture2.png"
size_hint: .3,.3
id: 2
pos: 200,200
MultitextureWidget:
"""
Builder.load_string(kv)
class MultitextureWidget(Widget):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.canvas = RenderContext()
# setting shader.fs to new source code automatically compiles it.
self.canvas.shader.fs = fs_multitexture
with self.canvas:
Color(1, 1, 1)
# here, we are binding a custom texture at index 1
# this will be used as texture1 in shader.
# The filenames are misleading: they do not correspond to the
# index here or in the shader.
BindTexture(source='mtexture2.png', index=1)
# create a rectangle with texture (will be at index 0)
Rectangle(size=(150, 150), source='mtexture1.png', pos=(500, 200))
# set the texture1 to use texture index 1
self.canvas['texture1'] = 1
# call the constructor of parent
# if they are any graphics objects, they will be added on our new
# canvas
super(MultitextureWidget, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# We'll update our glsl variables in a clock
Clock.schedule_interval(self.update_glsl, 0)
def update_glsl(self, *largs):
# This is needed for the default vertex shader.
self.canvas['projection_mat'] = Window.render_context['projection_mat']
self.canvas['modelview_mat'] = Window.render_context['modelview_mat']
class MultitextureLayout(FloatLayout):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.size = kwargs['size']
super(MultitextureLayout, self).__init__(**kwargs)
class MultitextureApp(App):
def build(self):
return MultitextureLayout(size=(600, 600))
if __name__ == '__main__':
MultitextureApp().run()
Image canvas/mtexture1.png¶
Image canvas/mtexture2.png¶